全文检索
概念

相当于是有两个步骤:
1、索:也就是建立索引,将一段文本进行相关的切分,形成许多词,同时记录出现的位置及次数
文本——》切分——-》词 文章出现过 出现多少次
2、检索:也就是查询。当我们输入一个关键词后,会去索引中进行搜索,返回符合条件的结果,并通过记录的出现的次数来进行相关度的排序
关键词——》索引中—–》符合条件的文章 相关度排序
特点

全文检索具有以下特点:
1、只处理文本,不处理语义
比如,搜索“你吃饭了吗?”只会进行文本的搜索,并不会返回“我吃了”。现在像百度,Google等,也有相关简单地语义处理,比如搜索“今天是几号”,可能会返回一个日历
2、搜索时英文不区分大小写
比如搜索“Spring”、“spring”、“SPRING”时返回的结果是一致的
3、结果列表有相关度排序
比如,搜索一个关键字时,那些内容显示在最前面,哪些排在后面
ElasticSearch
简介
什么是ElasticSearch

ElasticSearch的诞生

安装
传统方式安装
0、环境准备
(1)操作系统:常见的操作系统都可以,比如CentOS7.X+、Ubuntu、Windows、macOS。这里以Ubuntu为例
(2)安装JDK11.0+ 并配置环境变量。注意如果本机安装的版本是11版本以下,比如jdk8,也无需卸载重新安装,因为ES安装包中已经给我们预装了JDK
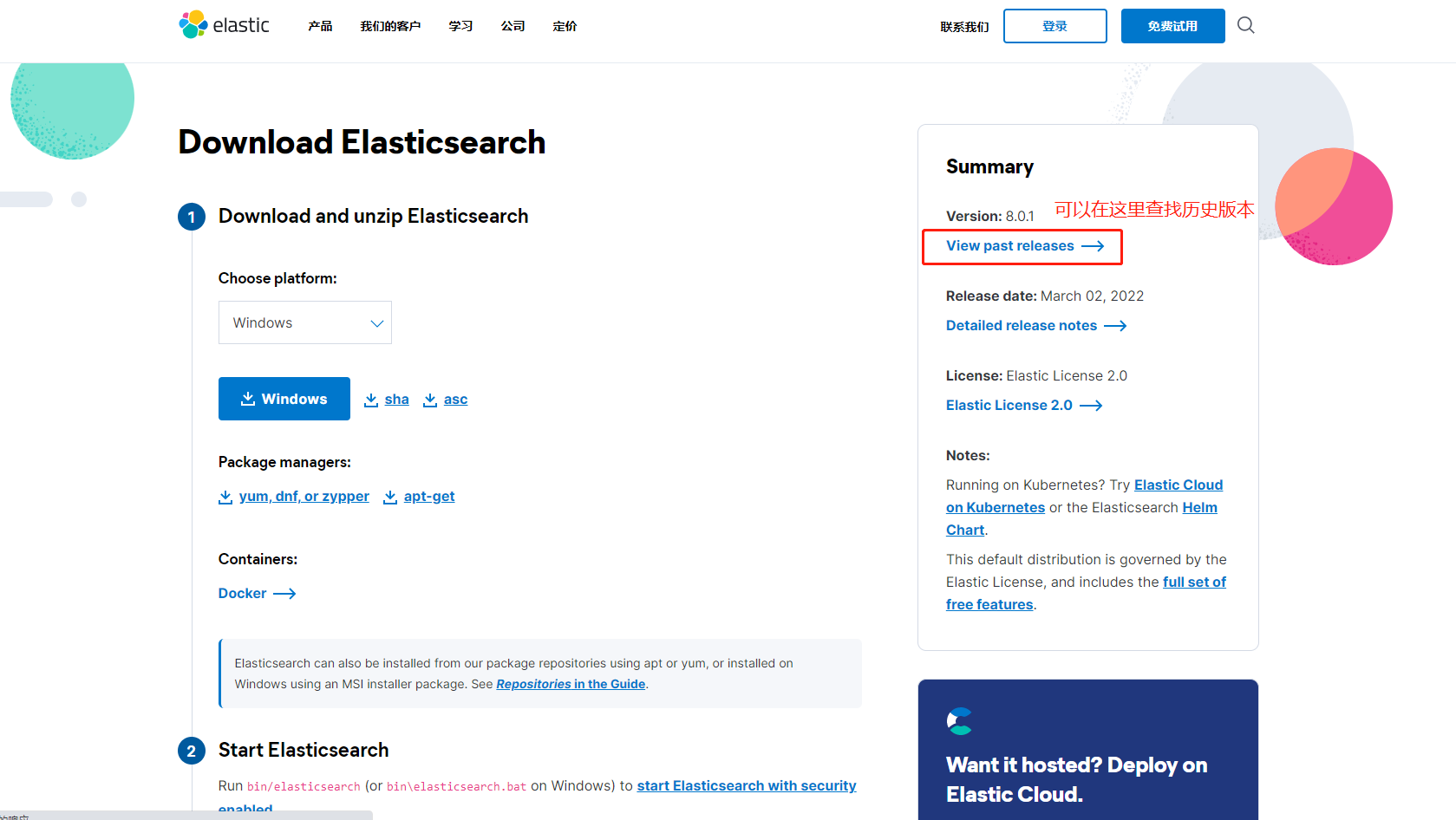
1、下载ES
https://www.elastic.co/cn/elasticsearch/
2、安装(注意:安装ES不能使用root用户,需要创建普通用户)
创建用户的命令如下:
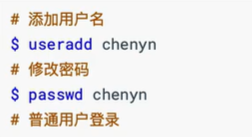
tips:如果命令行前面是$证明是普通用户,如果是#代表是root用户
3、用创建的普通用户进行解压缩操作
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-7.14.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
4、查看ES解压包中的目录结构
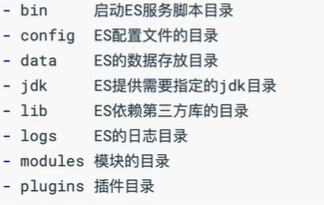
其中data目录在刚解压完成未运行时是没有的,需要运行后才有。
5、启动ES服务
使用普通用户,切换到ES安装目录下的bin目录中,直接输入命令./elasticsearch即可启动
meng@ubuntu:~/software/elasticsearch-7.14.0/bin$ ./elasticsearch
如果想后台启动,需要加参数-d
meng@ubuntu:~/software/elasticsearch-7.14.0/bin$ ./elasticsearch -d
启动成功后可以使用 ps -ef|grep elasticsearch 命令查看进程
如果此时你的电脑已经装有JDK,并且低于JDK11,那么将会抛出错误,并且可以使用以下两种方式解决:
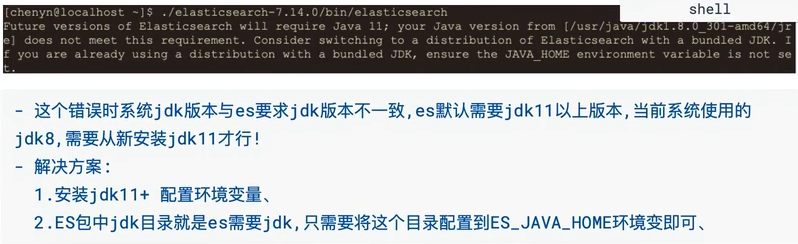
配置环境变量:
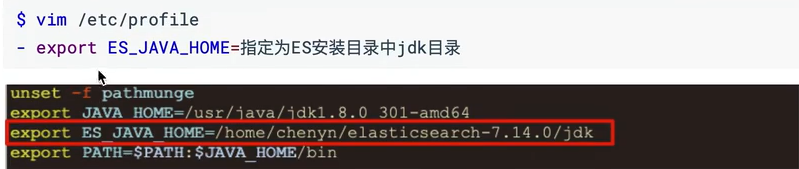
配置完成之后使用source /etc/profile命令重新加载,或者直接重启机器
source /etc/profile 重新加载
然后重新启动ES服务
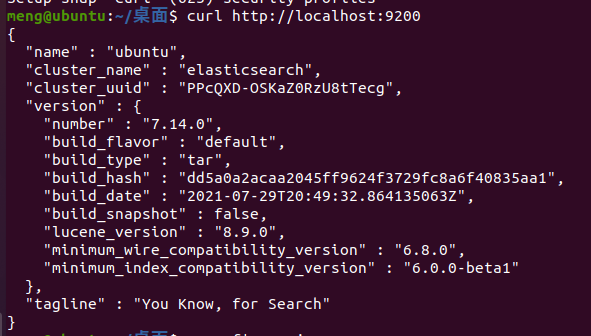
6、访问ES
默认启动的ES是无法通过外网进行访问的,可以通过Linux中的curl命令进行测试
http://localhost:9200
9200是web端口,也就是restful风格的端口,TCP的端口是9300
7、停止ES服务
正常的启动,可以在ES的启动窗口按CTRL+C结束进程。
如果是通过后台方式./elasticsearch -d启动的,可以配合进程搜索命令ps -ef|grep elasticsearch查看进程号,使用 kill -9 进程号 去杀死进程
8、开启远程访问

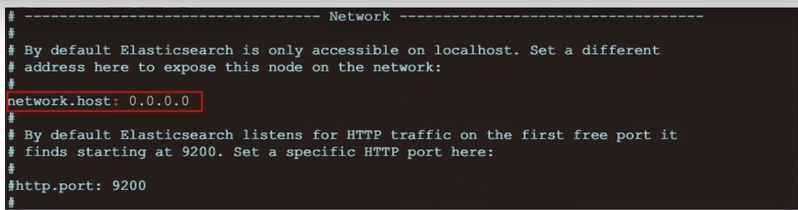
vim elasticsearch.yml
设置配置文件中的network.host属性,注意yml的语法格式,:后面需要有空格
network.host: 0.0.0.0
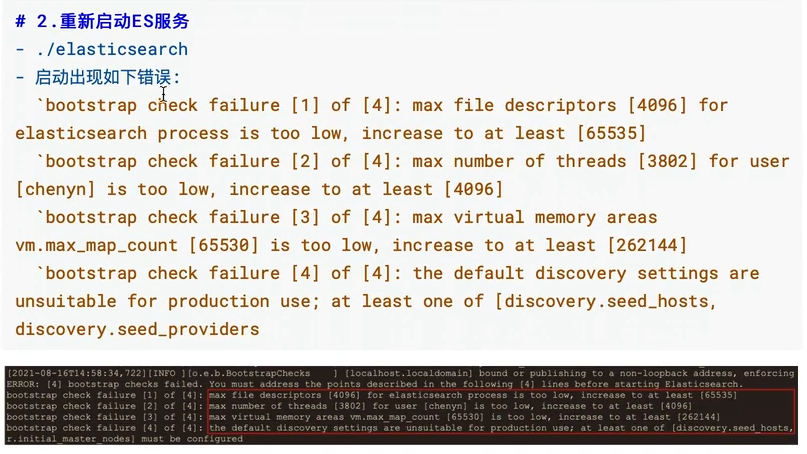
注意不同的Linux系统,报错可能会不同,注意分别解决即可


Docker方式安装

Kibana
简介

安装
传统方式安装
要注意下载的kibana版本要和ES版本保持一致,这里下载的是7.14.0,同时在安装kibana时,一定要注意启动ES
1、下载Kibana
https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/kibana
2、安装下载的Kibana
tar -zxvf kibana-7.14.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
3、编辑kibana的配置文件
vim /kibana安装目录/config/kibana.yml
4、修改如下配置
server.host: "0.0.0.0" #开启kibana的远程访问
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"] #配置ES的服务器地址
5、启动kibana
kibana安装目录/bin下执行
./kibana
6、访问kibana的web界面
http://地址:5601 #kibana默认端口为5601
如: http://192.168.11.128:5601/
docker方式安装

compose方式安装
核心概念

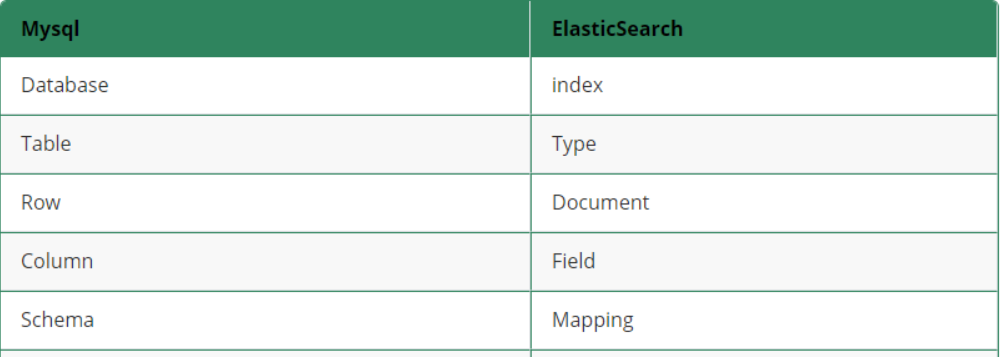
在ES7.X中索引相当于mysql中的表,mapping相当于mysql中的Schema主要存储字段的类型等信息,文档相当于mysql中的数据行。
这里说明几个概念:
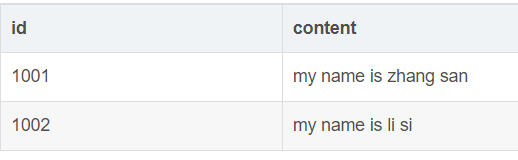
1、正排索引
像我们平时mysql中的数据行,第一行数据id为1001,内容是XXX
2、倒排索引
在ES中使用的是倒排索引,包含关键词name的有id为1001,1002的数据
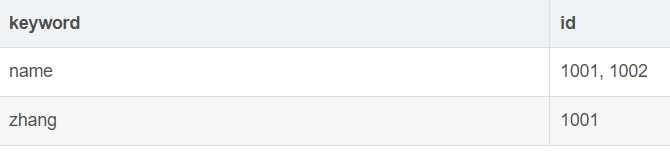
有了倒排索引,这样表的概念慢慢就弱化了,所以在ES7.X中就将原先Type的概念直接移除了,在ES7.X以前版本的对应关系
基本操作
索引
索引只能创建、查询、删除,不能修改
创建
1、创建索引
注意:
(1)ES中索引健康状态:
red(索引不可用)
yellow(索引可用,但存在风险)
green(索引健康)
(2)默认ES在创建索引时会为索引创建一个备份索引和一个primary索引
PUT /索引名 例如:PUT /products
这时候创建的索引健康状态为yellow,rep备份分片为1,因为主分片为1,副本分片为1 ,并且位于同一台机器上,会存在风险
2、创建索引,并进行索引分片配置
PUT /orders
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1, #指定主分片的数量
"number_of_replicas": 0 #指定副本分片的数量
}
}
此时创建的索引,健康状态为green
查询
#查看ES中的所有索引
GET /_cat/indices
#开启详细输出
GET /_cat/indices?v
删除
DELETE /索引名
例如:
DELETE /products
DELETE /* *代表通配符,代表所有索引
映射
ES中常见的字段类型:
具体详见https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.15/mapping-types.html

创建
映射的创建不能单独进行,必须在创建索引的时候,使用mapping字段去进行指定
#创建一个索引为products,mapping信息包含id,title,price,create_at,description
PUT /products
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "integer"
},
"title":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"price":{
"type": "double"
},
"create_at":{
"type": "date"
},
"description":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
查询
#查看某个索引的映射信息
GET /索引名/_mapping
例如:
GET /products/_mapping
需要注意:映射信息不允许修改,如果发现错误,只能将索引删除掉,然后重新建立索引和映射
文档
添加文档
#添加文档操作,手动指定文档id,ES中用_id字段存储ID
POST /products/_doc/1
{
"id":1,
"title":"小浣熊",
"price":0.5,
"created_at":"2022-12-11",
"description":"小浣熊真好吃"
}
#添加文档操作,自动生成文档id,是采用UUID生成的
POST /products/_doc
{
"title":"日本豆",
"price":1.5,
"created_at":"2022-12-11",
"description":"日本豆很不错"
}
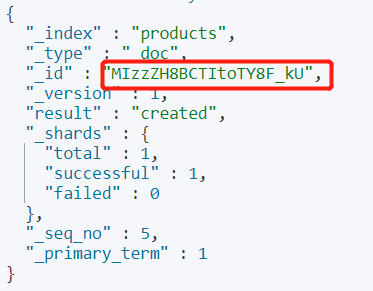
查询文档
#文档查询操作 基于id查询
GET /products/_doc/MIzzZH8BCTItoTY8F_kU

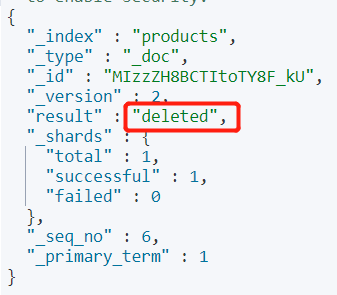
删除文档
#删除文档操作,基于id删除
DELETE /products/_doc/MIzzZH8BCTItoTY8F_kU
更新文档
#更新文档
这样更新的文档会删除原始文档,然后再重新添加,所以此时只有title一个属性
PUT /products/_doc/1
{
"title":"小浣熊1号"
}
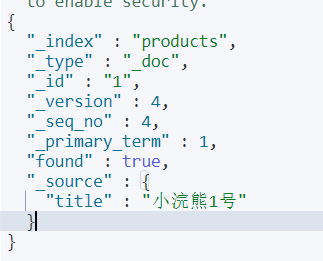
出现这种问题可以有两种方式解决:
#第一种方式
#在更新时,传递全部字段进行更新,将原先字段的内容传递过来
PUT /products/_doc/1
{
"title":"小浣熊1号",
"price":0.5,
"created_at":"2022-12-11",
"description":"小浣熊真好吃"
}

#第二种方式:这种方式会先根据ID将内容先查询出来,然后再去更新。可以将数据原始内容保存,并在此基础上进行更新
#更新操作,基于指定的字段进行更新
POST /products/_doc/1/_update
{
"doc":{
"price":1.6,
"title":"小浣熊"
}
}

批量操作
#文档批量操作
#批量添加,"index"代表的是添加操作,"_id"代表指定ID值,#{"index":{}}这样代表自动生成ID
POST /products/_doc/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{
"id":2,
"title":"小浣熊2号",
"price":2.5,
"created_at":"2022-12-11",
"description":"小浣熊2号真好吃"
}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{
"id":3,
"title":"小浣熊3号",
"price":3.5,
"created_at":"2022-12-11",
"description":"小浣熊3号真好吃"
}
这样直接会报错
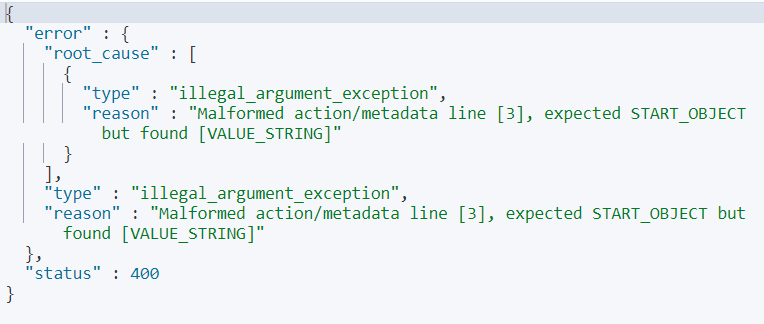
原因在于,如果是批量添加数据,不论数据多少,都不应格式化,应该在同一行
POST /products/_doc/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{"id":2,"title":"小浣熊2号","price":2.5,"created_at":"2022-12-11","description":"小浣熊2号真好吃"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"id":3,"title":"小浣熊3号","price":3.5,"created_at":"2022-12-11","description":"小浣熊3号真好吃"}

#更新操作,其中包括添加、更新、删除
POST /products/_doc/_bulk
{"index":{}}
{"title":"小浣熊4号","price":4.5,"created_at":"2022-12-11","description":"小浣熊4号真好吃"}
{"update":{"_id":3}}
{"doc":{"title":"小浣熊3号更新"}}
{"delete":{"_id":2}}
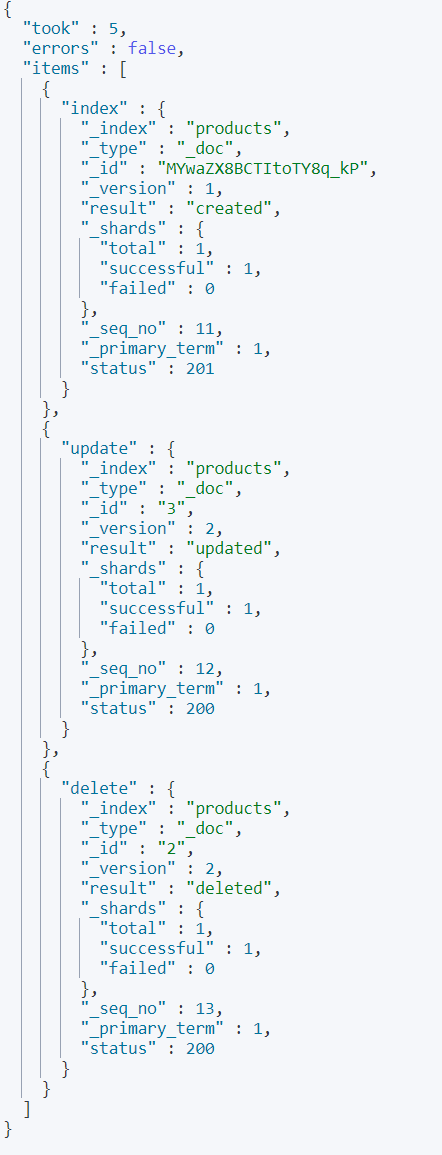
需要注意的是:虽然这是一个批量操作,但是每条结果都是单独返回的,也就是说他们之间每一条都是单独运行的,并不是一个原子操作,不会说因为某一条失败而全部失败
高级查询

语法
查询所有:[match_all]
match_all关键字:返回索引中的全部文档
GET /索引名/_doc/_search{json格式请求体数据}
或者可以简化成:
GET /索引名/_search{json格式请求体数据}
例如:
GET products/_doc/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{}
}
}
或者
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}

关键词查询[term]
term关键字:用来使用关键词查询
#基于关键字查询
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "小浣熊"
}
}
}
}
需要注意:
1、在ES的Mapping type中的keyword、date、integer、long、double、boolean、ip这些类型不分词,只有text类型分词。在上面创建products索引时,title的类型为keyword。所以title不会分词,只有查询的title值和数据值完全一致时才能查到,所以这里如果写成
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "浣熊"
}
}
}
}
那么将会查询不到结果
2、对于分词的字段,ES中默认使用标准分词器(StandardAnalyzer),即对于中文是单字分词,对英文是单词分词
例如,description字段是text类型,默认分词的
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "熊"
}
}
}
}
这样会查询出description中包含“熊”的,但是如果
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "好吃"
}
}
}
}
这样则查询不出结果,因为中文默认是单字分词
对于英文而言则是单词分词,比如插入一条文档,描述是“very good”
POST /products/_doc/6
{
"id":6,
"title":"小浣熊6号",
"price":5.5,
"created_at":"2022-12-11",
"description":"very good"
}
那么使用very或者good都可以查询到
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "very"
}
}
}
}
或者
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "very"
}
}
}
}
这两条查询语句都可以查询到
范围查询[range]
查询指定范围内的文档
#范围查询 gt大于 gte大于等于 lt小于 lte小于等于
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 0, #代表大于等于0,小于等于5
"lte": 5
}
}
}
}
前缀查询[prefix]
用来检索含有指定前缀的关键词的相关文档
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"title": {
"value": "小浣"
}
}
}
}
这里查询的title字段类型是keyword,是不分词的,所以这里以“小浣”开头的记录都能查到,但是如果换成查询description
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"description": {
"value": "小浣"
}
}
}
}
那么这里的description是text类型,是分词的,而且标准分词器默认中文是单字分词,既然是单字那么查询“小浣”开头的肯定是不存在,所以这样就查询不出记录,如果是英文是可以的,因为英文是单词分词
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"description": {
"value": "good" #或者"value": "g"或者"value": "go"等都可以
}
}
}
}
通配符查询[wildcard]
通配符查询:?用来匹配一个任意字符 *用来匹配多个任意字符
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"description": {
"value": "goo?" #匹配goo开头,后面只有一个字符,并且可以是任意字符
}
}
}
}
或者
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"description": {
"value": "go*" #匹配go开头,后面可以有多个,并且可以是任意字符
}
}
}
}
多id查询[ids]
值为数组类型,用来根据一组id获取多个对应的文档
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [1,2,3,4,5,6]
}
}
}
查询出id是1,2,3,4,5,6的
模糊查询[fuzzy]
用来模糊查询含有指定关键字的文档
需要注意:
fuzzy模糊查询,最大的模糊次数要在0-2之间
搜索关键词长度为2不允许存在模糊
搜索关键词长度为3-5允许模糊一次
搜索关键词长度大于5允许模拟两次
为了测试方便,这里先插入一条数据
POST /products/_doc/10
{
"id":10,
"title":"小浣熊牌干脆面",
"price":0.5,
"created_at":"2022-12-11",
"description":"小浣熊牌干脆面真好吃"
}
模糊查询,这里我们以title字段进行查询,title的字段长度为7,可以允许模糊两次
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": "小浣熊牌干脆面" #此时完全匹配可以查到
}
}
}
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": "小狗熊牌干脆面" #此时有一个字不同,也就是一次模糊,也可以查到
}
}
}
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": "小狗狗牌干脆面" #此时有两个字不同,也就是两次模糊,也可以查到
}
}
}
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": "小狗狗牌干干面" #此时有三个字不同,也就是三次模糊,不能查到
}
}
}
布尔查询[bool]
用来组合多个条件实现复杂的查询
must:相当于&&,要同时成立
| should:相当于 | ,成立一个就可以 |
must_not:相当于!,任何一个都不能满足
#查询ID为1并且title为“小浣熊”的记录
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"ids": {
"values": [1]
}
},{
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "小浣熊"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
多字段查询[multi_match]
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "小浣熊",
"fields": ["title","description"]
}
}
}
会用查询参数“小浣熊”分别去查询title字段和description字段
需要注意的是:
1、如果字段是不分词的,比如title字段,那么他就会把参数作为一个整体去查,比如这里会将“小浣熊”作为一个整体去title字段查询
2、如果字段是分词的,比如description字段,那么他就会按照分词规则将参数进行分词,因为这里是标准分词器,中文是单字分词,所以这里会将参数分为“小”,“浣”,“熊”三个,分别去description字段查询
所以
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "浣豆",
"fields": ["title","description"]
}
}
}
此时会去查title字段是“浣豆”的,还有description字段包含“浣”和包含“豆”的
默认字段分词查询[query_string]
定义一个默认字段,如果字段是分词的,那么查询条件将会分词分词后进行查询,如果字段不分词,那么查询条件也将不分词进行查询
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"default_field": "title",
"query": "豆熊"
}
}
}
title是keyword类型不分词的,那么将会查询title是“豆熊”的
如果
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"default_field": "description",
"query": "豆熊"
}
}
}
description是text类型是分词的,那么将会查询description中有“豆”、“熊”的
高亮查询[highlight]
可以让符合条件的文档中的关键字高亮显示。
需要注意的是,ES中的高亮显示并不是在原始文档中直接修改,而是放到了highlight属性中,并不会修改原始数据,所以以后我们在进行程序处理的时候,还需要将原始数据中的内容进行替换
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "小浣熊"
}
}
},{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "熊"
}
}
}
]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"*":{} #这里代表将查询出来的所有字段都进行高亮显示,也可以指定字段"title":{}
}
}
}
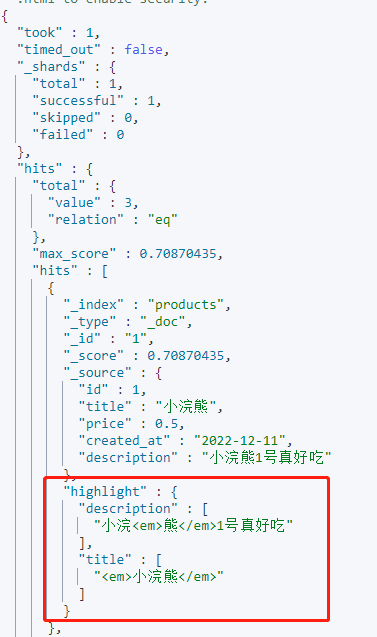
以上示例可以看到ES默认使用标签将高亮内容进行了修饰,我们也可以进行标签的自定义
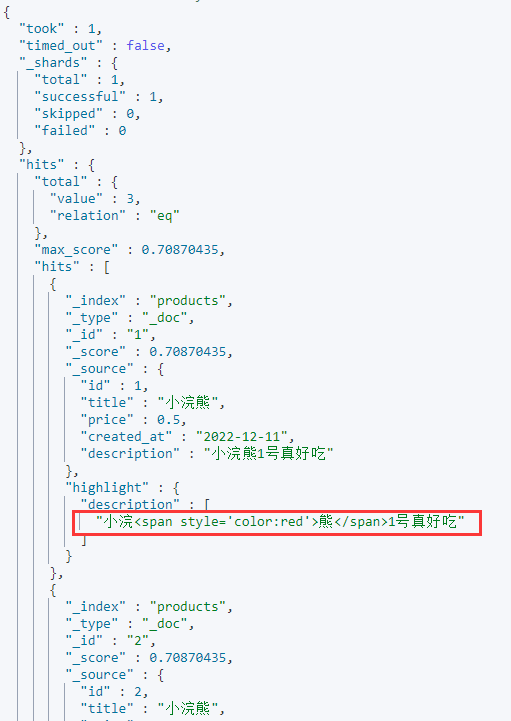
#使用pre_tags和post_tags自定义高亮HTML标签
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "小浣熊"
}
}
},{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "熊"
}
}
}
]
}
}
, "highlight": {
"pre_tags": ["<span style='color:red'>"],
"post_tags": ["</span>"],
"fields": {
"description": {}
}
}
}
默认highlight中的分词字段只能是参与查询的字段,但是如果想让所有的字段都高亮显示,可以使用require_field_match开启多个字段高亮
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "熊"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": ["<span style='color:red'>"],
"post_tags": ["</span>"],
"require_field_match": "false",
"fields": {
"*": {}
}
}
}
这样所有的字段都可以进行高亮显示,但是ES7中只有分词的字段类型才能够参与高亮显示。
例如,我们新建一个索引,此时description1,description2都是text类型,都是分词的
PUT /orders
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "integer"
},
"title":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"description1":{
"type": "text"
},
"description2":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
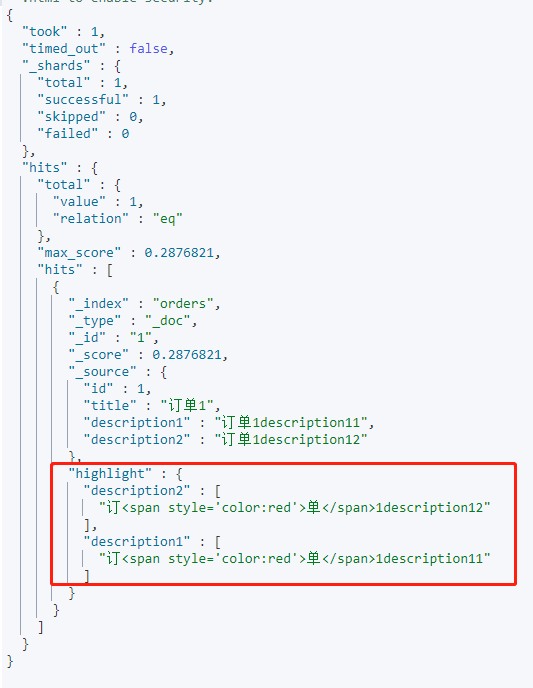
然后我们插入一条数据
POST /orders/_doc/1
{
"id":1,
"title":"订单1",
"description1":"订单1description11",
"description2":"订单1description12"
}
我们进行查询时高亮显示,让多个字段都高亮显示
GET /orders/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description1": {
"value": "单"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": ["<span style='color:red'>"],
"post_tags": ["</span>"],
"require_field_match": "false",
"fields": {
"*": {}
}
}
}
返回指定条数[size]
指定查询结果中返回指定条数,默认返回值是10条
#指定返回两条数据,类似于mysql中的每页返回条数
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 2
}
分页查询[from]
用来指定起始返回位置,和size关键字连用可以实现分页效果
#从第0条开始,返回两条数据
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0, #这里数值的计算和mysql一样。(当前页-1)*size
"size": 2
}
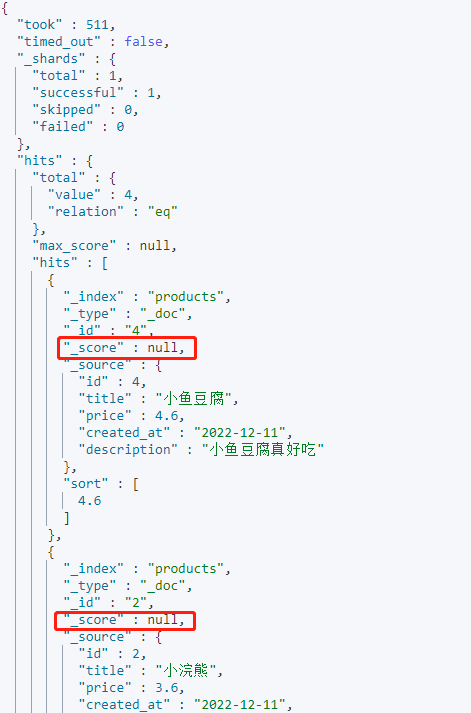
指定字段排序[sort]
#以价格进行排序
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc" #升序asc
}
}
]
}
我们手动指定排序的时候,会干预默认ES的搜索,所以我们查询出来的所有文档得分都不存在
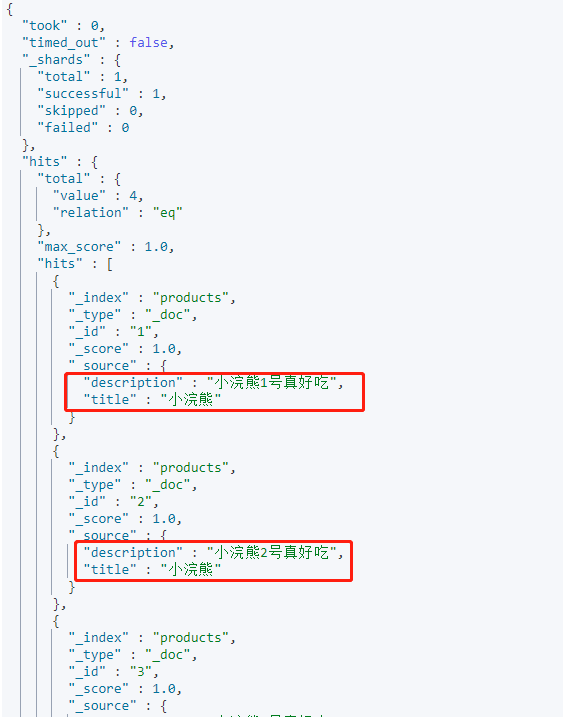
返回指定字段[_source]
是一个数组,在数组中指定展示哪些字段,默认ES会返回所有的字段
#查询出来的结果只显示"title","description"两个字段
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": ["title","description"]
}
索引原理
倒排索引

索引模型
我们先创建一个索引及映射,现有索引和映射如下
PUT /products1
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"description":{
"type": "text"
},
"price":{
"type": "float"
},
"title":{
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
插入如下数据
| _id | title | price | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蓝月亮洗衣液 | 19.9 | 蓝月亮洗衣液很高效 |
| 2 | iphone13 | 19.9 | 很不错的手机 |
| 3 | 小浣熊干脆面 | 1.5 | 小浣熊很好吃 |
#使用批量添加的方式
PUT /products1/_doc/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"title":"蓝月亮洗衣液","price":19.9,"description":"蓝月亮洗衣液很高效"}
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{"title":"iphone13","price":19.9,"description":"很不错的手机"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"title":"小浣熊干脆面","price":1.5,"description":"小浣熊很好吃"}
在存储以上这些数据的时候,ES内部是这样实现的:
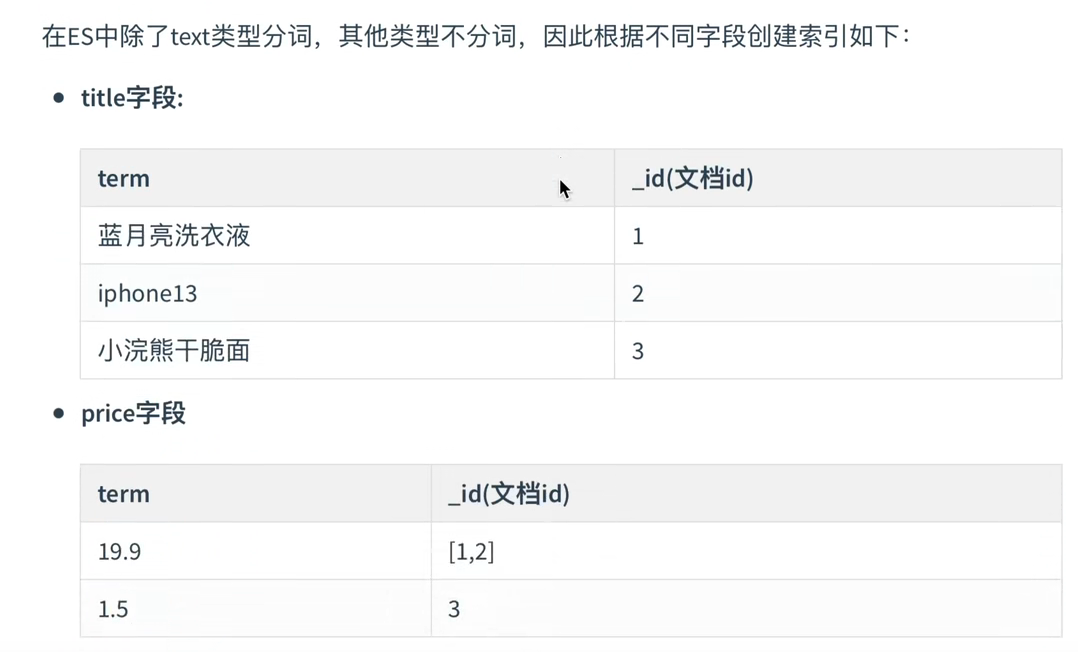
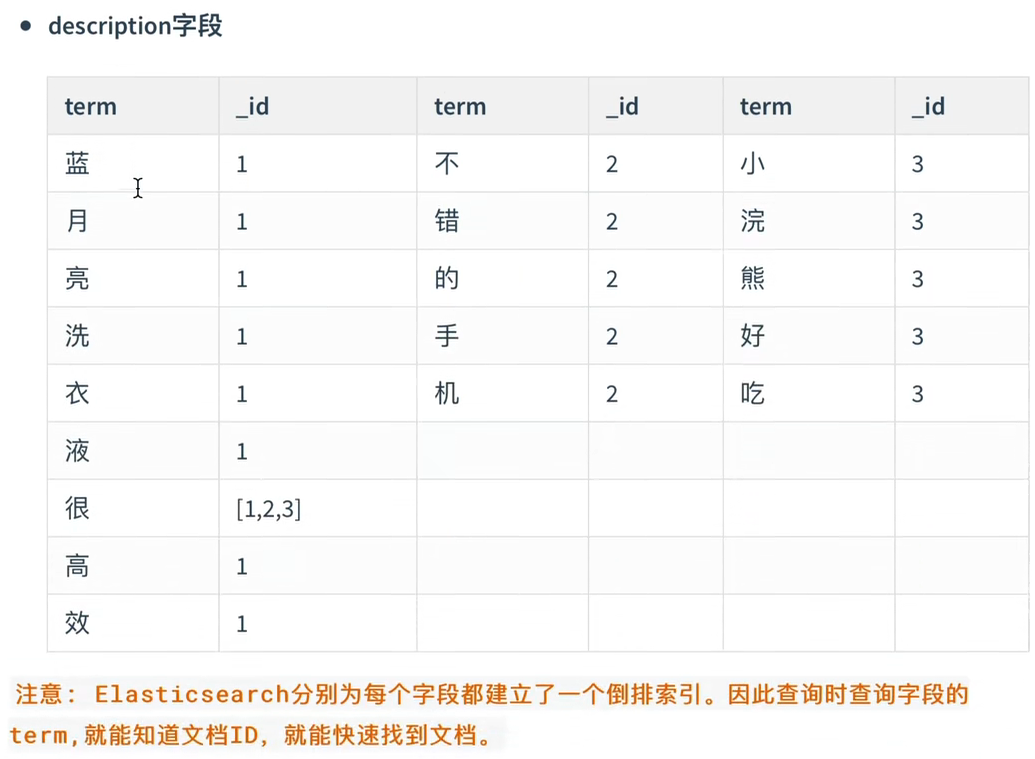
综合以上用图例表示为:

除此以外,ES不光会记录文档的id,还会值在文档中出现的次数以及文档的长度,用于计算出_score的值用作排序,比如以上的”很“字在三条文档中都会出现,那么ES中会做如下记录:
| id | 出现次数 | 文档长度 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 1 | 6 |
| 3 | 1 | 6 |
可以看出ID为2和3的文档权值应该是相同的,ID为1的权限较低一点(10个长度才出现1次,所以值会低一点),所以在查询“很”字时,ES会默认将ID为2和3的显示在前面
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "很"
}
}
}
}

分词器
Analysis和Analyzer

Analyzer组成

内置分词器

内置分词器测试
标准分词器
特点:按照单词分词,英文统一转为小写,过滤标点符号,中文单字分词
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "this is a , good Man 中华人民共和国"
}

Simple分词器
特点:英文按照单词分词,英文统一转为小写,去掉标点符号,中文按照空格进行分词
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "simple",
"text": "this is a , good Man 中华人民 共和国"
}

Whitespace分词器
特点:中文、英文按照空格进行分词,英文不会转成小写,不去掉标点符号
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "whitespace",
"text": "this is a , good Man 中华人民 共和国"
}

创建索引设置分词
PUT test1
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "keyword" #指定使用何种分词器
}
}
}
}
添加一条记录
PUT /test1/_doc/1
{
"title":"小黑,is good man!"
}
查询:因为指定了分词器是keyword,会将输入的内容当做一整个词语,不会进行分割,所以需要这样才能查询到
GET /test1/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "小黑,is good man!" #因为不会分割,所以需要搜索输入的整个内容
}
}
}
}
中文分词器
在ES中支持的中文分词器非常多,比如smartCN、IK等,推荐使用IK分词器
安装IK分词器
开源分词器IK的GitHub:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
需要注意的是:
- IK分词器的版本要与你安装的ES版本保持一致。这里使用的是7.14.0
1、下载对应版本
最好新建一个文件夹,比如ik,然后在文件夹中进行下载解压
wget https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v7.14.0/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.14.0.zip
2、解压
解压zip文件,需要先安装unzip
yum install -y unzip
unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.14.0.zip
3、移动到es安装目录中的plugins目录中
mv 要移动的文件夹 移动到那个位置(路径要根据自己现在的位置改变)
mv ik ./plugins/
ik分词器中包含的文件
4、重启ES生效
5、本地安装IK分词器配置目录为:
ES安装目录/plugins/ik/config/IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml
IK使用

#ik_smart 最粗粒度的拆分
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "中华人民共和国国歌"
}

#ik_max_word 最细粒度的拆分
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "中华人民共和国国歌"
}

以后在创建索引时,如何指定ik分词器呢?
和上面一样
PUT test2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word" #指定使用何种分词器
}
}
}
}
拓展词、停用词配置


例如:
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "大家好,我叫小明明"
}
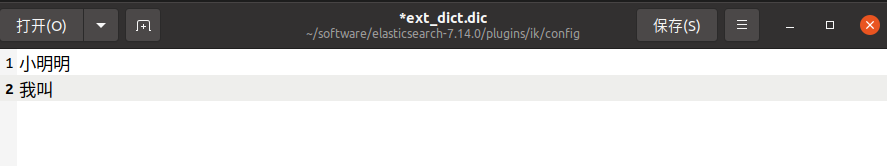
此时默认是没有“小明明”、“我叫”这两个词组的

可以通过设置拓展词加入,注意:每行只能写一个词
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "大家好,我叫小明明"
}
再次测试发现,拓展词加入了

停用词正好相反,可以让本该出现的词不出现,比如将上面例子中的“明明”停用
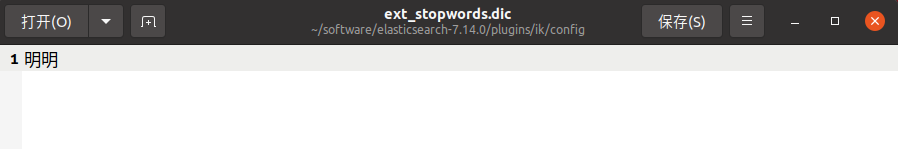 日常使用中可以停用的词和拓展的词都会很多,如果自己一个个加入会很麻烦,所以IK分词器默认给我们建立了很多的默认词典。我们可以在他的基础上在进行修改即可
日常使用中可以停用的词和拓展的词都会很多,如果自己一个个加入会很麻烦,所以IK分词器默认给我们建立了很多的默认词典。我们可以在他的基础上在进行修改即可
过滤查询
过滤查询

使用
# 要配合着bool查询来使用
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match_all": {}} #查询条件
],
"filter": {} #过滤条件
}
}
}
注意:
- 在执行 filter 和 query 时,先执行filter,再执行query
- Elasticsearch会自动缓存经常使用的过滤器,以加快性能
类型
常见的过滤类型有:term、terms、range、exists、ids等filter
为了做示例我们先创建一个索引
# 创建索引及映射
PUT /products1
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"description":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word" #指定成ik分词器的一种方式
},
"price":{
"type": "float"
},
"title":{
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
#添加数据,采用批量添加的方式
PUT /products1/_doc/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"title":"蓝月亮洗衣液","price":19.9,"description":"蓝月亮洗衣液很高效"}
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{"title":"iphone13","price":19.9,"description":"很不错的手机"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"title":"小浣熊干脆面","price":1.5,"description":"小浣熊很好吃"}
{"index":{"_id":4}}
{"title":"辣条","price":1.5,"description":"辣条很好吃"}
{"index":{"_id":5}}
{"title":"大饼","price":1.5,"description":"大饼很好吃"}
term过滤
# term过滤
#先过滤出来description有“好吃”的,然后再过滤的基础上查询所有,所以会将description字段中有“好吃”的全部查询出来
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_all": {}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"term": {
"description": "好吃"
}
}
]
}
}
}

#term过滤
#先过滤出来description有“好吃”的,然后再过滤的基础上查询description有"浣熊"的,所以会将description字段中有“好吃””浣熊“的查询出来
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "浣熊"
}
}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"term": {
"description": "好吃"
}
}
]
}
}
}

terms过滤
#terms过滤,先过滤出description字段中包含"浣熊","洗衣液","辣条"的,在此基础上查询所有
需要注意,使用IK分词器,像"洗衣液","辣条"需要拓展才能查询到
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_all": {}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"terms": {
"description": [
"浣熊",
"洗衣液",
"辣条"
]
}
}
]
}
}
}

range 过滤
# range过滤,先过滤出0<=price<=10的,然后在这个基础上,查询description包含辣条的
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "辣条"
}
}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 0,
"lte": 10
}
}
}
]
}
}
}

exists 过滤
过滤存在指定字段的记录,获取指定字段不为空的索引记录
# range过滤,先过滤出存在“description”字段的记录,然后查询出“description”中包含“辣条”的
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "辣条"
}
}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"exists": {
"field": "description"
#"field": "aaa" 如果这边指定一个不存在的字段,比如“aaa”,那么将过滤不出记录
}
}
]
}
}
}
ids 过滤
过滤含有指定id的记录
# ids过滤,先过滤出id为1、2、3的,然后在此基础上查询“description”字段中包含“洗衣液”的
GET /products1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "洗衣液"
}
}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"ids": {
"values": [
"1",
"2",
"3"
]
}
}
]
}
}
}

整合应用
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置客户端
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.client.ClientConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.client.RestClients;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.config.AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration;
@Configuration
public class RestClientConfig extends AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration {
@Override
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {
final ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = ClientConfiguration.builder()
//修改成ES服务的地址,当然这边的配置可以转移到配置文件里面
.connectedTo("localhost:9200")
.build();
return RestClients.create(clientConfiguration).rest();
}
}
客户端对象
我们通过以上的配置与ES建立连接之后,在Spring的工厂中会存在以下两个对象
- ElasticSearchOperations
- RestHighLevelClient 推荐
我们可以通过任意一个对象去操作ES,那么ElasticSearchOperations是通过对象的方式去操作ES ,RestHighLevelClient则是通过rest方式操作ES,和kibana中操作ES很像
ElasticSearchOperations
特点:始终使用面向对象的方式操作ES
建立索引及映射
/**
* @Document 作用在类上,将这个类对象转为es中一条文档进行录入
* indexName:用来指定文档的索引名称
* createIndex:用来指定是否创建索引
*/
@Document(indexName = "products",createIndex = true)
public class Product {
//@Id作用在属性上,将对象id字段与ES中文档的_id对应
@Id
private Integer id;
/**@Field作用在属性上,用来描述属性在ES中存储类型以及分词情况
* --type用来指定字段类型
*/
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String title;
@Field(type = FieldType.Double)
private Double price;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String description;
//生成set/get
}
新增文档
通过ElasticsearchOperations的save方法
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchOperations elasticsearchOperations;
@Test
public void testInsert() {
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1);
product.setTitle("小浣熊干脆面");
product.setPrice(1.5);
product.setDescription("小浣熊干脆面很好吃");
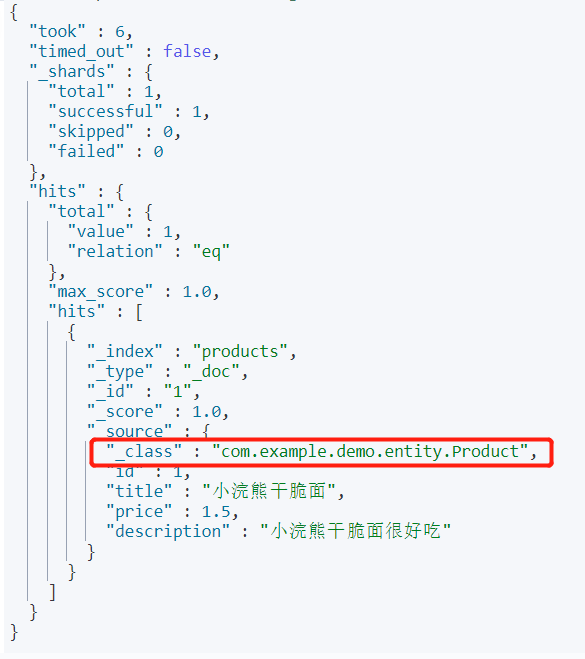
elasticsearchOperations.save(product);
}
}
通过这种方式添加的文档会有_class字段,记录文档的类型,用于后面反序列化时,反序列化何种类型
更新文档
也是通过ElasticsearchOperations的save方法
//save方法当文档id不存在时添加文档,当文档id存在时更新文档
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1);
product.setTitle("小浣熊");
product.setPrice(1.5);
product.setDescription("小浣熊干脆面很好吃");
elasticsearchOperations.save(product);
}
查询
//查询一条文档
@Test
public void testQuery() {
Product product = elasticsearchOperations.get("1", Product.class);
System.out.println(product.getId()+product.getTitle());
}
//查询所有
@Test
public void testQueryAll() throws JsonProcessingException {
SearchHits<Product> productSearchHits = elasticsearchOperations.search(Query.findAll(), Product.class);
System.out.println("最高分数:"+productSearchHits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("总条数:"+productSearchHits.getTotalHits());
for (SearchHit<Product> productSearchHit:productSearchHits){
//将查询出来的内容转换成json格式
System.out.println(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(productSearchHit.getContent()));
}
}
删除文档
//删除一条
@Test
public void testDelete() {
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1);
elasticsearchOperations.delete(product);
}
//删除所有
@Test
public void testDeleteAll() {
elasticsearchOperations.delete(Query.findAll(),Product.class);
}
RestHighLevelClient
类似于在kibana中操作ES
创建索引及映射
/**
* 因为我们上面配置完成,和ES建立连接之后会自动生成ElasticSearchOperations和RestHighLevelClient两个对象,所以这里我们直接
*注入使用就可以
*/
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
//在kibana中
PUT products
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"price":{
"type": "double"
},
"create_at":{
"type": "date"
},
"description":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
//在java中
@Test
public void testRestInsert() throws IOException {
//指定创建索引的名称
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("product");
/**
* 这里的索引结构可以直接从kibana中写好复制过来,
* 当然如果只是创建索引及映射完全可以在kibana中操作,这里也是为了测试
* mapping方法创建索引,参数1:指定映射的JSON结构 参数2:指定数据类型
*/
createIndexRequest.mapping("{\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"title\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"double\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"create_at\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"date\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }", XContentType.JSON);
//create方法,参数1:创建索引请求对象 参数2:请求配置对象
CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = restHighLevelClient.indices().create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("索引创建状态:"+createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged());
restHighLevelClient.close();
}
删除索引
//在kibana中
DELETE /products
//在java中
@Test
public void testRestDelete() throws IOException {
DeleteIndexRequest deleteIndexRequest = new DeleteIndexRequest("product");
AcknowledgedResponse delete = restHighLevelClient.indices().delete(deleteIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("删除状态:" + delete.isAcknowledged());
}
创建文档
//在kibana中
PUT /product/_doc/1
{
"title":"小浣熊",
"price":"1.5",
"create_at":"2022-01-01",
"description":"小浣熊很好吃"
}
//在java中
@Test
public void testRestInsertDoc() throws IOException {
//指定操作那个索引
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("product");
indexRequest.id("1");//手动指定文档id,不指定会自动生成UUID形式的
//source方法,参数1:索引请求对象 参数2:请求配置对象
indexRequest.source("{\"tittle\":\"小浣熊\",\"price\":\"1.5\",\"create_at\":\"2022-01-01\",\"description\":\"小浣熊很好吃\"}",XContentType.JSON);
IndexResponse indexResponse = restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("文档创建状态:"+indexResponse.status());
}
更新文档
//在kibana中
POST /product/_doc/1/_update
{
"doc":{
"title":"小浣熊干脆面"
}
}
//在java中
@Test
public void testRestUpdateDoc() throws IOException {
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("product","1");
updateRequest.doc("{\"title\":\"小浣熊干脆面\"}",XContentType.JSON);
UpdateResponse updateResponse = restHighLevelClient.update(updateRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("更新文档状态:"+updateResponse.status());
}
删除文档
//在kibana中
DELETE /product/_doc/1
//在java中
@Test
public void testRestDeleteDoc() throws IOException {
DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("product", "1");
DeleteResponse deleteResponse = restHighLevelClient.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("删除文档状态:"+deleteResponse.status());
}
基于ID查询文档
//在kibana中
GET /product/_doc/1
//在java中
@Test
public void testRestFindByIdDoc() throws IOException {
GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("product", "1");
GetResponse getResponse = restHighLevelClient.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("id:"+getResponse.getId());
System.out.println("source的String形式:"+getResponse.getSourceAsString());
Map<String, Object> source = getResponse.getSource();
System.out.println(source.get("title"));
}
查询所有
//在kibana中
GET /product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
//在java中
@Test
public void testMatchAll() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");//指定搜索的索引
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());//查询所有
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);//指定查询条件
//这里返回的响应对象就是对下面图片中结果的封装,取值的时候可以对照着下面图片
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
//这块取值可以对照着下面的图片,在返回结果中有一个hits数组,hits数组中还有一个hits数组,在下面才是每一个hit对象
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}

term查询
@Test
public void testTerm() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//和上面的查询相比,只需要更换查询条件,其他不需要变
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description","浣熊"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
经过以上两个查询,可以发现只有查询条件不同,其他代码都相同,那么我们可以抽象出一个方法
//抽象出一个方法,将查询条件作为参数传递
public void query(QueryBuilder queryBuilder) throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");//指定搜索的索引
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(queryBuilder);//查询所有
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);//指定查询条件
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
这样抽象出方法后,以后所有的参数查询都可以借助这个方法
@Test
public void testQuery() throws IOException {
//1、查询所有
//query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
//2、term 关键词查询
//query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description","辣条"));
//3、range 范围查询 1<price<=3
//query(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").gt(1).lte(3));
//4、prefix 前缀查询
//query(QueryBuilders.prefixQuery("title","小浣熊"));
//5、wildcard 通配符查询 ?代表一个字符 *代表任意多个字符
//query(QueryBuilders.wildcardQuery("title","小*"));
//6、ids 多个指定id查询
//query(QueryBuilders.idsQuery().addIds("1","2","3"));
//或者可以这样写
//query(QueryBuilders.idsQuery().addIds("1").addIds("2").addIds("3"));
//7、multi_match 多字段查询
query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("非常好吃小浣熊","title","description"));
}
分页查询
//在kibana中,from指定从第几页开始,size指每页显示条数
GET /product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 1
}
//在java中 from size
@Test
public void testSearch() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
sourceBuilder.from(0);//起始位置
sourceBuilder.size(1);//每页显示条数
//也可以链式调用
// sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery()).from(0).size(1);
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
排序
//在kibana中,使用sort实现,这里在上个分页例子的基础上排序
GET /product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}
//在java中,sort
@Test
public void testSearch() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
sourceBuilder.from(0);//起始位置
sourceBuilder.size(10);//每页显示条数
sourceBuilder.sort("price", SortOrder.ASC);//排序,参数1:按哪个字段排序 参数2:排序方式
// 也可以链式调用
// sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery()).from(0).size(10).sort("price", SortOrder.ASC);
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
显示指定字段
//在kibana中,使用_source实现,这里在上个例子的基础上实现
GET /product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
],
"_source": ["title","description"]
}
//在java中 fetchSource
@Test
public void testSearch() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
sourceBuilder.from(0);//起始位置
sourceBuilder.size(10);//每页显示条数
//排序,参数1:按哪个字段排序 参数2:排序方式
sourceBuilder.sort("price", SortOrder.ASC);
//fetchSource 参数1:指定显示字段数组 参数2:指定排除字段数组
// sourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"title","description"},new String[]{});//只显示title、description两个字段
sourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{},new String[]{"create_at"});//不显示create_at字段
// 也可以链式调用
// sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery())
// .from(0)
// .size(10)
// .sort("price", SortOrder.ASC)
// .fetchSource(new String[]{},new String[]{"create_at"});
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
高亮显示
//这里我们重新创建索引,并将title字段设置成分词类型的text
//删除索引
DELETE /product
//重新创建
PUT product
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"price":{
"type": "double"
},
"create_at":{
"type": "date"
},
"description":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
//插入数据
PUT /product/_doc/1
{
"title":"小浣熊",
"price":"1.5",
"create_at":"2022-01-01",
"description":"小浣熊很好吃"
}
PUT /product/_doc/2
{
"title":"豆腐",
"price":"3.5",
"create_at":"2022-01-01",
"description":"豆腐很好吃"
}
PUT /product/_doc/3
{
"title":"辣条",
"price":"2.5",
"create_at":"2022-01-01",
"description":"辣条很好吃"
}
//在kibana中使用highlight指定
GET /product/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "好吃"
}
}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
],
"highlight": {
"require_field_match": "false",
"pre_tags": ["<span style='color:red'>"],
"post_tags": ["</span>"],
"fields": {"description": {},"title": {}}
}
}
//在java中 highlighter
@Test
public void testSearch() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//高亮条件的构造
HighlightBuilder highlightBuilder = new HighlightBuilder();
highlightBuilder.requireFieldMatch(false).field("title").field("description").preTags("<span style='color:red;'>").postTags("</span>");
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description","豆腐"));
sourceBuilder.from(0);//起始位置
sourceBuilder.size(10);//每页显示条数
sourceBuilder.sort("price", SortOrder.ASC);//排序,参数1:按哪个字段排序 参数2:排序方式
sourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{},new String[]{"create_at"});//不显示create_at字段
sourceBuilder.highlighter(highlightBuilder);
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
//在取得高亮的显示时,可以对照下图的JSON结构
Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields();
if(highlightFields.containsKey("description")) {
System.out.println("description高亮结果:"+highlightFields.get("description").fragments()[0]);
}
if(highlightFields.containsKey("title")) {
System.out.println("title高亮结果:"+highlightFields.get("title").fragments()[0]);
}
}
}

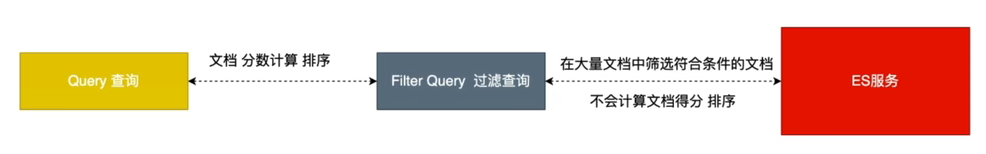
过滤查询
ES中的查询分为两种,query和filter query
query:精确查询,查询并计算文档的得分,并根据文档得分进行返回
filter query:过滤查询,用来在大量的数据中筛选出符合条件的数据,不会计算文档的得分,对于一些经常使用的filter query会对结果进行缓存
注意:一旦使用了query和filter query,那么ES会优先执行filter query,在过滤的基础上再执行query
@Test
public void filterQuery() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("product");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());//在过滤的基础上再查询所有
//sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description","浣熊"));//在过滤的基础上再查询出description中包含“浣熊”的
//指定过滤条件
//sourceBuilder.postFilter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description","豆腐"));//过滤description字段中包含“豆腐”字段的
//sourceBuilder.postFilter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").gt(0).lte(3));//过滤出0<price<=3的
//sourceBuilder.postFilter((QueryBuilders.existsQuery("title")));//过滤出存在title字段的
sourceBuilder.postFilter(QueryBuilders.idsQuery().addIds("1","2","3"));//过滤出ID为1、2、3的
//searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
for(SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println("id: "+hit.getId()+" source:"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
restHighLevelClient操作对象
新建一个索引
PUT /goods
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "integer"
},
"title":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"price":{
"type": "double"
},
"description":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
创建相关的实体类
public class Goods {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private Double price;
private String description;
//生成set/get以及toString
}
操作
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoGoods {
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
//插入数据
@Test
public void testInsert() throws IOException {
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setId(1);
goods.setTitle("小浣熊干脆面");
goods.setPrice(1.5);
goods.setDescription("小浣熊干脆面很好吃");
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("goods");
indexRequest.id(goods.getId().toString());
//这里通过jackson下面的ObjectMapper对象将对象转换成json
//这里我们原先直接传递的JSON串,这里可以将对象转成JSON串后传入,便于我们直接操作对象
indexRequest.source(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(goods), XContentType.JSON);
IndexResponse indexResponse = restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(indexResponse.status());
}
//查询操作
@Test
public void testQuery() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("goods");
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
searchSourceBuilder.from(0).size(30);//分页
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
List<Goods> goods = new ArrayList<>();
for (SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
//将JSON转换成对象
Goods good = new ObjectMapper().readValue(hit.getSourceAsString(), Goods.class);
goods.add(good);
}
for (Goods good:goods) {
System.out.println(good);
}
}
//如果查询的数据有高亮字段
@Test
public void testHighLighter() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("goods");
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
HighlightBuilder highlightBuilder = new HighlightBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description","浣熊"));
searchSourceBuilder.from(0).size(30);//分页
highlightBuilder.requireFieldMatch(false).field("description").preTags("<span style='color:red;'>").postTags("</span>");
searchSourceBuilder.highlighter(highlightBuilder);
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("总条数:"+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
System.out.println("最大得分:"+searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore());
SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
List<Goods> goods = new ArrayList<>();
for (SearchHit hit:hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
//将JSON转换成对象
Goods good = new ObjectMapper().readValue(hit.getSourceAsString(), Goods.class);
//处理高亮
Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields();
//如果存在高亮字段则设置
if(highlightFields.containsKey("description")) {
good.setDescription(highlightFields.get("description").fragments()[0].toString());
}
goods.add(good);
}
for (Goods good:goods) {
System.out.println(good);
}
}
}

聚合查询
简介

测试数据
#创建索引及映射
PUT /fruit
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"price":{
"type": "double"
},
"description":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
#添加测试数据
PUT /fruit/_bulk
{"index":{}}
{"title":"面包","price":19.9,"description":"小面包非常好吃"}
{"index":{}}
{"title":"旺仔牛奶","price":29.9,"description":"旺仔牛奶非常好喝"}
{"index":{}}
{"title":"日本豆","price":19.9,"description":"日本豆非常好吃"}
{"index":{}}
{"title":"小馒头","price":19.9,"description":"小馒头非常好吃"}
{"index":{}}
{"title":"大辣片","price":39.9,"description":"大辣片非常好吃"}
{"index":{}}
{"title":"透心凉","price":9.9,"description":"透心凉非常好喝"}
{"index":{}}
{"title":"小浣熊","price":19.9,"description":"童年的味道"}
{"index":{}}
{"title":"海苔","price":19.9,"description":"海的味道"}
Kibana中使用
根据某个字段分组
#根据price字段,统计数量
#这里的price_group是任意起的名字
GET /fruit/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"price_group": {
"terms": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
#当然也可以根据条件查询后在进行分组
GET /fruit/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "非常"
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"price_group": {
"terms": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}

如果不想返回所有的数据,可以通过设置size实现
#通过设置size:0不让返回所有数据
GET /fruit/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"price_group": {
"terms": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}

最大值
GET /fruit/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"max_price": {
"max": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
最小值
GET /fruit/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"min_price": {
"min": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
求和
GET /fruit/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"sum_price": {
"sum": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
平均值
GET /fruit/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"avg_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
Springboot中应用
基于字段进行聚合查询
package com.example.demo;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.AggregationBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.AggregationBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.Aggregations;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.bucket.terms.ParsedDoubleTerms;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.bucket.terms.ParsedStringTerms;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.bucket.terms.Terms;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoAggs {
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
//基于字段的聚合查询,桶中的值是键值对的形式
@Test
public void testAggs() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("fruit");
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());//查询条件
// searchSourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.terms("price_group").field("price"));//设置聚合处理
searchSourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.terms("title_group").field("title"));//设置聚合处理
searchSourceBuilder.size(0);
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
Aggregations aggregations = searchResponse.getAggregations();
//这里price返回的是double类型,可以直接使用ParsedDoubleTerms接收
// ParsedDoubleTerms doubleTerms = aggregations.get("price_group");
// List<? extends Terms.Bucket> buckets = doubleTerms.getBuckets();
//这里的title是String类型的,那么就可以使用ParsedStringTerms接收
ParsedStringTerms stringTerms = aggregations.get("title_group");
List<? extends Terms.Bucket> buckets = stringTerms.getBuckets();
// for(Terms.Bucket bucket:buckets) {
//获取桶中的键值对
// System.out.println("价格:"+bucket.getKey()+"--数量:"+bucket.getDocCount());
// }
for(Terms.Bucket bucket:buckets) {
System.out.println("名称:"+bucket.getKey()+"--数量:"+bucket.getDocCount());
}
}
}
MAX MIN AVG SUM
//max(ParsedMax) min(ParsedMin) sum(ParsedSum) avg(ParsedAvg)
//桶中只有一个返回值
@Test
public void testAggsFunction() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("fruit");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.max("max_price").field("price"));//max
sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.min("min_price").field("price"));//min
sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.sum("sum_price").field("price"));//sum
sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.avg("avg_price").field("price"));//avg
sourceBuilder.size(0);
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
Aggregations aggregations = searchResponse.getAggregations();
ParsedMax parsedMax = aggregations.get("max_price");//取得最大值
ParsedMin parsedMin = aggregations.get("min_price");//取得最小值
ParsedSum parsedSum = aggregations.get("sum_price");//求和
ParsedAvg parsedAvg = aggregations.get("avg_price");//平均值
//桶中只有一个返回值,直接取值即可
System.out.println("最大值"+parsedMax.getValue());
System.out.println("最小值"+parsedMin.getValue());
System.out.println("求和"+parsedSum.getValue());
System.out.println("平均值"+parsedAvg.getValue());
}





